I. Introduction
The Future Unleashed: Why Electric Vehicles are better than Petrol and Diesel
The need to fight climate change and lessen environmental effect has become crucial as the world prepares for a sustainable revolution.
Electric vehicles have become huge advantages in this time of upheaval, giving a cleaner, greener, and more powerful option in contrast to petroleum and diesel cars. Electric vehicles have shown their value through enhancements in innovation, foundation, and government support, catching the interest of purchasers, organizations, and state run administrations the same. This comprehensive article delves into the myriad reasons why electric vehicles surpass their traditional counterparts in numerous aspects. From environmental benefits to economic advantages, performance enhancements to public health improvements, the advantages of electric vehicles are far-reaching and diverse. Through an exploration of the latest technological advancements, government policies, and charging infrastructure developments, we uncover the full potential of electric vehicles as catalysts for change.
Go along with us as we investigate the interesting universe of electric vehicles and break down what they mean for our economy, biology, and generally speaking way of life.
Realize the reason why electric vehicles are the eventual fate of transportation as well as the establishment for a world that is economical and flourishing for people in the future.

II. Environmental Impact
Traditional petrol and diesel automobiles pose significant environmental problems, which must be addressed by using electric vehicles. The shift towards electric mobility presents a myriad of environmental benefits, significantly contributing to a cleaner and greener future.
A. Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
We can significantly slow down climate change by substituting electric motors powered by clean energy sources for internal combustion engines.
B. Improved Air Quality
Electric vehicles help to decrease brown haze, respiratory illnesses, and general natural weakening by eliminating exhaust contaminations like nitrogen dioxide (NO2) and particulate matter (PM).
C. Mitigating Climate Change
Electric vehicles are a valuable instrument for lessening the impacts of environment change. They are urgent in assisting with decarbonizing the transportation business by bringing down the reliance on fossil fuels. In request to diminish fossil fuel byproducts and slow the climb in worldwide temperatures, the vehicle area should make extensive decreases in its commitment to worldwide ozone harming substance outflows.
D. Lowering Carbon Footprint
The carbon footprint of electric vehicles extends beyond their usage. When contrasted with petroleum and diesel vehicles, electric vehicles have a diminished generally carbon impression regardless of whether they might utilize power created from various sources, including fossil fuels. The carbon force of the power framework falls as environmentally friendly power sources multiply, making electric vehicles all the more biologically gainful after some time.
E. Decreasing Dependence on Fossil Fuels
Electric vehicles provide a pathway towards reducing our dependence on finite and polluting fossil fuels. Electric vehicles may be charged with clean, sustainable energy thanks to the incorporation of renewable energy sources into the electrical system. This transition promotes energy diversification and enhances energy security, freeing us from the uncertainties and environmental risks associated with fossil fuel extraction and combustion.
In conclusion, electric vehicles present an appealing solution to the urgent environmental issues of our day.
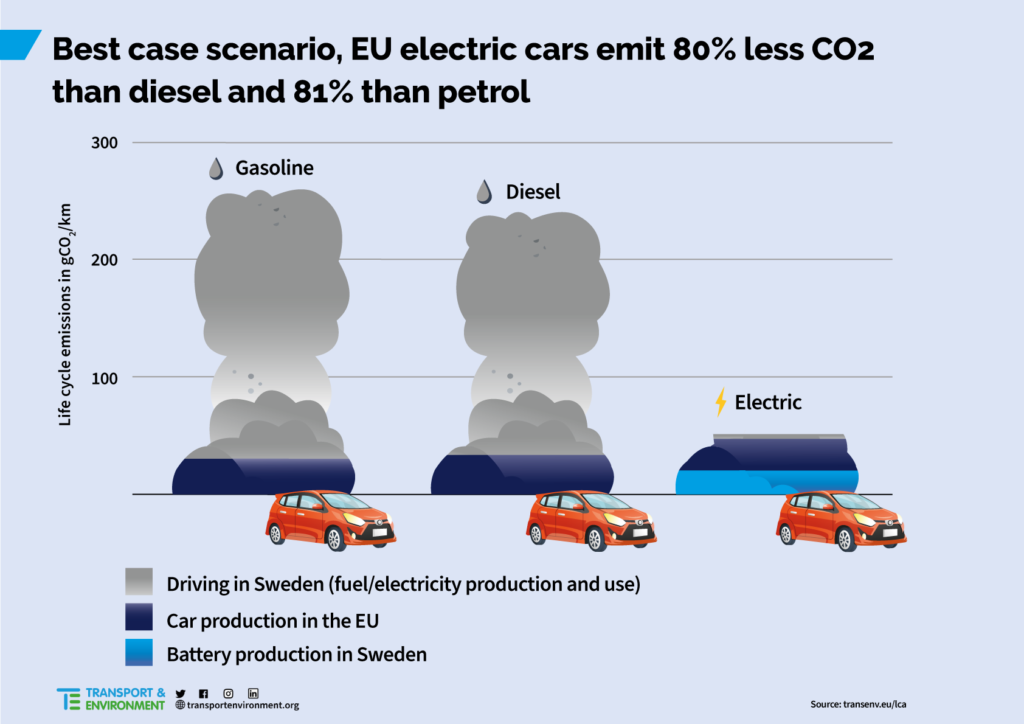
III. Economic Advantages
Embracing electric vehicles goes beyond environmental benefits; they also offer significant economic advantages that have the potential to revolutionize the transportation industry and drive sustainable economic growth.
A. Long-term Cost Savings
Electric vehicles present an opportunity for substantial long-term cost savings. Albeit the underlying expense of an electric vehicle might be more than that of a petroleum or diesel vehicle, the general expense of responsibility for course of the vehicle’s lifetime is regularly lower. Electric vehicles cost less to keep up with and fix since they have less moving parts and require less maintenance. Additionally, there are extra monetary advantages on the grounds that the cost of the power expected to drive electric vehicles is normally more affordable than the cost of petroleum or diesel.
B. Lower Maintenance and Operational Costs
Electric vehicles have fewer components prone to wear and tear compared to traditional vehicles with internal combustion engines. This translates to lower maintenance costs over time, as electric vehicles do not require frequent oil changes, spark plug replacements, or exhaust system repairs. The simplicity of electric vehicle drivetrains contributes to their reliability and reduced need for costly repairs.
C. Reduced Fuel Expenses
Electric vehicles offer a significant advantage in terms of fuel expenses. Electricity is frequently less expensive to refuel a diesel or petrol vehicle than to charge an electric vehicle. Additionally, the stability of electricity prices compared to the volatile nature of fossil fuel prices provides more predictable and potentially lower fuel costs for electric vehicle owners. This makes it possible for both people and companies to allocate resources and manage their transport expenditures more effectively.
D. Job Creation and Economic Growth
The inescapable utilization of electric vehicles can possibly support the economy and produce new position amazing open doors. The electric vehicle industry requires a diverse range of skilled workers, including engineers, technicians, battery manufacturers, and charging infrastructure installers. This demand for a skilled workforce stimulates job creation and helps build a robust ecosystem of electric vehicle-related industries, from manufacturing and supply chain management to research and development. Furthermore, the development of framework for electric vehicles, for example, charging stations and matrix mix frameworks, sets out speculation open doors and advances monetary development at the nearby, provincial, and public levels. Societies may leverage the potential for long-term cost savings, lower fuel costs, job creation, and overall economic growth by utilising the economic benefits of electric vehicles. This transition not only transforms the transportation sector but also lays the foundation for a sustainable and prosperous future.
E. Technological Advancements
Electric vehicles drive technological advancements in the automotive industry, stimulating innovation and fostering economic growth. The development of battery innovation, charging foundation, and refined frameworks are only a couple of the ventures that have profited from the improvement of electric vehicle innovation.
F. Energy Independence
Transitioning to electric vehicles reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy independence for countries. By utilizing domestically generated electricity or renewable energy sources, nations can reduce their reliance on foreign oil imports, thereby improving energy security and mitigating economic vulnerabilities associated with fluctuations in global fuel prices.
G. Infrastructure Development Opportunities
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles presents opportunities for infrastructure development. The installation of charging stations and the expansion of charging networks create new business prospects and jobs in construction, electrical services, and technology sectors. Moreover, the deployment of charging infrastructure in public spaces, commercial areas, and residential communities stimulates economic activity in these locations, attracting consumers and driving local businesses.
H. Reduced Externalities
Petrol and diesel vehicles impose significant external costs on society, including health-related expenses due to air pollution and environmental damages caused by greenhouse gas emissions. By transitioning to electric vehicles, these externalities can be reduced, leading to cost savings for healthcare systems and avoiding environmental remediation costs. The overall economic impact of reducing externalities associated with traditional vehicles contributes to long-term economic stability and sustainability. Electric vehicles offer a promising economic outlook by driving technological innovation, fostering energy independence, creating infrastructure development opportunities, and reducing external costs. Adopting electric mobility not only provides businesses and individuals with immediate cash gains, but it also boosts overall economic development and improves societal well-being.
IV. Energy Efficiency
With a few advantages regarding energy change, usage, and waste decrease, electric vehicles are hailed as an additional energy-effective option in contrast to petroleum and diesel cars.
A. Utilizing Energy More Effectively
Contrasted with vehicles fueled by gas powered motors, electric vehicles are characteristically more energy-efficient. Through heat scattering in the motor and fumes framework, traditional vehicles waste a significant measure of energy. In contrast, electric vehicles convert electrical energy from the battery to kinetic energy more efficiently, with minimal energy loss.
B. Higher Energy Conversion Rates
Electric motors used in electric vehicles have high energy conversion rates, typically around 90%, meaning they can convert a larger portion of the electrical energy from the battery into actual motion. In contrast, internal combustion engines in petrol and diesel vehicles have lower conversion rates, typically below 40%, as a considerable portion of energy is lost as heat.
C. Reducing Energy Waste and Losses
Electric vehicles also minimize energy waste and losses during operation. Electric vehicles can collect and store energy that would often be lost as heat during braking thanks to regenerative braking systems.The car can then be powered by this energy or the battery can be recharged, increasing overall efficiency and extending the range.
D. Energy Management Systems
Advanced energy management systems in electric vehicles optimize energy utilization and distribution. These systems intelligently manage the power flow between the battery, motor, and auxiliary systems, ensuring efficient use of energy based on driving conditions, vehicle demands, and user preferences. By optimizing energy consumption, electric vehicles maximize their efficiency and contribute to overall energy conservation.
E. Overcoming Energy Inefficiencies of Fossil Fuel Supply Chain
Energy efficiency throughout the entire supply chain is a benefit of electric automobiles. While the extraction, refinement, transportation, and distribution of fossil fuels for traditional vehicles result in energy losses and inefficiencies, electric vehicles directly utilize electricity, which can be generated from various sources with varying efficiencies. The energy proficiency of electric vehicles keeps on expanding as the power lattice utilizes more environmentally friendly power sources.
Electric vehicles demonstrate superior energy efficiency through effective utilization of energy, higher conversion rates, minimized waste, and optimized energy management systems. We can make huge strides towards a more practical and energy-effective transportation framework by embracing electric versatility.
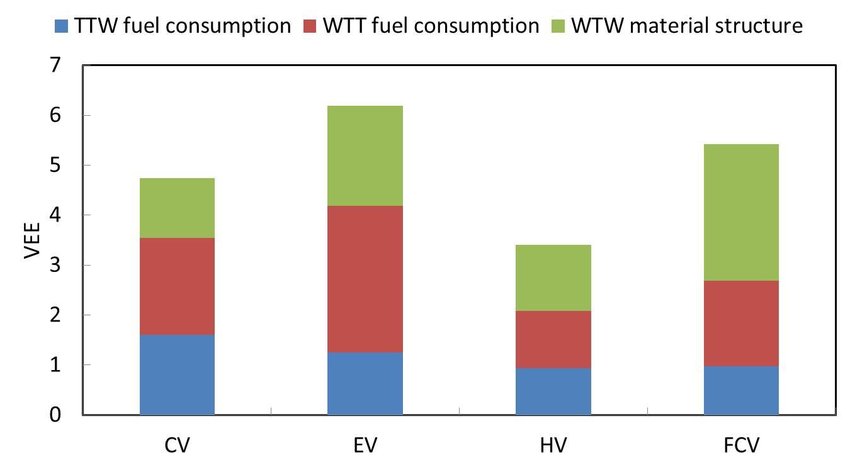
V. Performance and Driving Experience
Electric vehicles not only excel in terms of environmental impact and economic advantages but also offer a compelling and exhilarating driving experience. With their advanced technology and unique characteristics, electric vehicles are redefining the standards of performance on the road.
A. Instant Torque and Acceleration
Electric vehicles are renowned for their impressive acceleration and instant torque delivery. Electric motors generate maximum torque from the moment they start, providing quick and seamless acceleration. This instantaneous power delivery contributes to a thrilling driving experience, allowing electric vehicles to outperform many petrol and diesel vehicles in terms of acceleration and responsiveness.
B. Smooth and Silent Operation
Electric vehicles operate silently, creating a serene and peaceful driving environment. Electric vehicles offer a quiet and smooth ride in contrast to the noise and vibrations produced by conventional internal combustion engines, improving passenger comfort and lowering noise pollution. This quiet operation also allows drivers to enjoy music, conversations, and the surrounding environment without disturbances.
C. Low Center of Gravity and Handling
Because of the enormous battery packs being put at the lower part of the vehicle, electric vehicles much of the time have a low focus of gravity. This configuration improves stability, cornering capabilities, and overall handling. The weight distribution of electric vehicles contributes to a balanced and agile driving experience, making them enjoyable to maneuver on various road conditions.
D. Regenerative Braking and Energy Recovery
This technology not only extends the driving range but also enhances control and efficiency. By recovering energy that would otherwise be wasted as heat, regenerative braking systems improve overall energy utilization and contribute to a more efficient driving experience.
E. Enhanced Technology and Connectivity
Electric vehicles often feature advanced technology and connectivity options. Touchscreen displays, smartphone integration, and voice-activated controls offer intuitive and convenient access to navigation, entertainment, and vehicle settings. Additionally, modern safety features, autonomous driving skills, and over-the-air software updates are frequently included in electric vehicles, improving both convenience and safety.
F. Expanding Charging Infrastructure
As the adoption of electric vehicles continues to grow, charging infrastructure networks are rapidly expanding. The availability of public charging stations and the convenience of home charging options provide peace of mind to electric vehicle owners, ensuring they can easily access charging facilities and maintain a reliable driving experience. Really long travel is made more advantageous and practical for electric vehicles because of the proceeded with improvement of super quick charging innovations. Electric vehicles offer an exhilarating driving experience characterized by instant torque, smooth operation, enhanced handling, regenerative braking, advanced technology, and a rapidly expanding charging infrastructure. Driving an electric vehicle isn’t just a capable choice for the climate yet in addition a thrilling and satisfying experience on the open street because of continuous upgrades in electric vehicle innovation.
VI. Public Health Benefits
By lessening air contamination and raising by and large air quality, the utilization of electric vehicles well affects individuals’ wellbeing and prosperity both by and by and aggregately.
A. Reduction in Air Pollutants
The reduction in air contamination is one of the primary benefits of electric vehicles for general wellbeing.
We can decisively decrease these perilous contaminations by changing to electric vehicles, which will bring about cleaner and better air for all.
B. Decreased Health Risks
The reduction in air pollutants from electric vehicles directly translates to decreased health risks for individuals. By minimizing exposure to pollutants emitted by petrol and diesel vehicles, electric vehicles contribute to improved respiratory health and a lower risk of associated illnesses, leading to a healthier population overall.
C. Mitigation of Noise Pollution
Another public health benefit of electric vehicles is the mitigation of noise pollution. The high noise levels in metropolitan areas are a result of the noise pollution produced by petrol and diesel automobiles.
The nature of rest, emotional wellness, and general prosperity may be in every way adversely affected by this commotion contamination. Electric vehicles, with their quiet operation, significantly reduce noise pollution, creating a more peaceful and tranquil environment for individuals and communities.
D. Enhanced Livability in Urban Areas
Electric vehicles contribute to the enhanced livability of urban areas. With reduced air and noise pollution, cities become more attractive and conducive to a high quality of life. Cleaner air promotes outdoor activities, encourages active transportation, and creates healthier environments for children and vulnerable populations. The transition to electric vehicles is consistent with the objective of building livable, sustainable cities that put citizens’ wellbeing first.
E. Social Equity and Environmental Justice
Electric vehicles have the potential to address social equity and environmental justice concerns. By and large, minimized individuals have been lopsidedly impacted by the negative wellbeing impacts of air pollution.We can progress ecological equity by guaranteeing cleaner air and better wellbeing results for all, paying little mind to financial level or geographic area, by diminishing air contaminations using electric vehicles.
The public health benefits of electric vehicles encompass cleaner air, reduced health risks, mitigation of noise pollution, enhanced livability, and improved social equity. By putting electric transportation first, we can build inclusive, healthy communities where people can prosper and live better lives.
VII. Technological Advancements
A new era of innovation, efficiency, and sustainability has begun thanks in large part to the development of electric vehicles, which are the driving force behind technological developments in the automotive sector.
A. Battery Technology
Electric vehicles have propelled significant advancements in battery technology. Manufacturers and researchers continue to develop batteries with higher energy densities, longer range capabilities, and faster charging speeds. These developments not only boost the efficiency and range of electric cars, but they also have uses in other industries like grid-scale energy systems, portable devices, and renewable energy storage.
B. Charging Infrastructure
The rise of electric vehicles has accelerated the development of charging infrastructure. The availability of charging stations is expanding, and several charging methods such Level 2 AC chargers, DC fast chargers, and wireless charging technology are all accessible.In order to manage energy consumption, optimise charging efficiency, and enable two-way energy flow between electric vehicles and the electrical grid, smart charging solutions and grid integration systems are also being developed.
C. Vehicle-to-Grid Integration
Innovation enhancements take into consideration vehicle-to-matrix (V2G) joining, which permits electric vehicles to both use and return abundance energy to the lattice. This concept opens up possibilities for energy storage, grid stabilization, and demand response programs. Electric vehicles can serve as mobile energy resources, supporting a more flexible and resilient electrical grid.
D. Autonomous Driving
The forefront of independent driving innovation is electric vehicles. The progression of independent driving innovation and high level driver help frameworks (ADAS) is generally modifying the way in which we view transportation. Electric vehicles are ideal for autonomous driving applications due to their electric drivetrains and cutting-edge sensors. This innovation can possibly increment street proficiency, decrease gridlock, and further develop wellbeing.
E. Connected Features
Electric vehicles offer a range of connected features that enhance the driving experience. Navigation, real-time updates, and remote vehicle management are all made possible through integrated infotainment systems, smartphone connectivity, and vehicle-to-infrastructure communication. These connected features provide convenience, improve safety, and enable data-driven insights for personalized driving experiences and maintenance optimization.
F. Lightweight Materials and Aerodynamics
To maximize range and energy efficiency, electric vehicles are driving advancements in lightweight materials and aerodynamic design. High-strength materials, such aluminum compounds and carbon fiber composites, can be utilized to lessen vehicle weight while protecting primary integrity. Streamlined optimal design limit air obstruction, further upgrading energy proficiency and broadening the driving scope of electric vehicles.Electric vehicles keep on pushing the limits of mechanical headways, moving advancement in battery innovation, charging foundation, vehicle-to-matrix mix, independent driving, associated highlights, lightweight materials, and streamlined features. A more sustainable and technologically sophisticated future is being shaped by these advances, which not only improve the performance and capacities of electric vehicles but also have broad ramifications for other industries.
VIII. Range and Charging Infrastructure
Range anxiety and the availability of charging infrastructure have long been key considerations for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. However, advancements in range capabilities and the expanding charging infrastructure are addressing these concerns, making electric vehicles more convenient and practical for everyday use.
A. Increasing Range Capabilities
The working scope of electric vehicles has fundamentally expanded over time. Electric vehicles presently have more noteworthy driving reaches thanks to progresses in battery innovation, making them a useful substitute for both short-and extremely long travel. Many electric vehicle models can achieve ranges that meet or exceed the average daily commuting needs of most individuals. Furthering the range of electric vehicles, lowering range anxiety, and broadening their consumer appeal are the main goals of continuing research and development.
B. Fast-Charging Technology
Electric vehicle charging is being revolutionised by fast-charging technologies. DC fast chargers, also known as Level 3 chargers, can replenish the battery capacity significantly faster compared to traditional Level 2 AC chargers. These well-placed fast-charging stations enable owners of electric vehicles to swiftly charge their vehicles when they are on longer travels or are in a rush. They are situated alongside major highways, in urban areas, and in well-known locations. Electric vehicles are now more practical and convenient for long travels and road trips thanks to the advent of ultra-fast charging technologies like 350 kW chargers, which further cut down on charging periods.
C. Home and Workplace Charging
Home and workplace charging options provide convenience and accessibility for electric vehicle owners. Home charging stations, in some cases alluded to as Even out 2 chargers, let proprietors of electric vehicles charge their vehicles while they rest or aren’t utilizing them. This ensures that the vehicle will be completely energized and accessible for use the next day. Workplace charging stations offer a similar benefit, allowing employees to conveniently charge their vehicles while at work. The availability of these charging options adds flexibility and peace of mind to electric vehicle ownership, reducing reliance on public charging infrastructure.
D. Public Charging Network
The public charging network continues to expand rapidly, with charging stations becoming more prevalent in urban areas, commercial centers, and along major transportation routes. Public charging stations provide an essential charging solution for electric vehicle owners who require on-the-go charging. They offer a range of charging speeds, from standard Level 2 chargers to DC fast chargers, catering to different needs and requirements. The overall availability and accommodation of claiming an electric vehicle is worked on by the rising thickness of public charging framework, which likewise simplifies it for drivers to find and utilize charging stations.
E. Charging Network Collaboration
Collaboration among different charging network providers is crucial for seamless charging experiences. Roaming agreements and interoperability standards enable electric vehicle owners to access charging stations across different networks with a single payment method or subscription. These collaborations ensure that electric vehicle drivers have a wide choice of charging options and can easily navigate different charging networks without facing compatibility issues. Such collaborations promote the growth of a cohesive and user-friendly charging infrastructure ecosystem.
F. Smart Charging Solutions
Smart charging solutions optimize the utilization of charging infrastructure and manage energy demand. These solutions employ advanced algorithms and data analytics to dynamically control and distribute charging power, considering factors such as grid load, renewable energy availability, and charging station utilization. By intelligently managing charging sessions, smart charging solutions maximize the efficiency and reliability of the charging infrastructure while minimizing the strain on the electrical grid.
The continuous advancements in range capabilities, the proliferation of fast-charging technology, the availability of home and workplace charging options, the expansion of the public charging network, collaborative efforts among charging network providers, and the implementation of smart charging solutions are collectively revolutionizing the range and charging infrastructure for electric vehicles. These developments alleviate range anxiety, enhance convenience, and contribute to the overall feasibility and practicality of electric vehicle ownership.

IX. Government Policies and Incentives
Incentives and legislation from the government are essential for encouraging the use of electric vehicles and facilitating the switch to a sustainable transportation system. These actions plan to energize buyers, organizations, and producers to embrace electric portability by giving monetary motivations, laying out administrative structures, and putting resources into framework development. A assortment of guidelines and motivators have been set up by legislatures all around the world to rush the reception of electric vehicles. Some common examples include:
- Purchase Incentives: State run administrations offer monetary motivating forces, for example, refunds or tax breaks, to decrease the forthright expense of buying an electric vehicle. These incentives make electric vehicles more affordable and attractive to consumers, stimulating demand and market growth.
- Charging Infrastructure Development: Governments invest in the development of charging infrastructure, including the installation of public charging stations, to address range anxiety and ensure convenient access to charging facilities. Funding programs and partnerships with private companies help expand the charging network, particularly in urban areas and along major transportation corridors.
- Zero-Emission Vehicle (ZEV) Mandates: ZEV requirements have been introduced by some governments, requiring automakers to develop and sell a specific proportion of zero-emission cars, including electric vehicles, in their fleets of vehicles. These mandates encourage manufacturers to prioritize electric vehicle production, driving innovation and market competitiveness.
- Emissions Standards and Regulations: Governments enforce stricter emissions standards and regulations, setting emission targets for vehicles. Electric vehicles, being zero-emission vehicles, help automakers meet these standards and avoid penalties. This approach encourages manufacturers to invest in electric vehicle technology and phase out vehicles with higher emissions.
- Incentives for Charging Infrastructure Installation: Governments provide incentives and grants to support the installation of private and workplace charging infrastructure. These incentives help businesses and individuals offset the costs of installing charging stations, promoting the expansion of charging infrastructure beyond public networks.
- Tax and Toll Benefits: Some governments offer tax benefits, reduced vehicle registration fees, or exemptions from road tolls for electric vehicle owners. These measures provide additional financial incentives and cost savings, making electric vehicle ownership more appealing. Government policies and incentives create a supportive environment for electric vehicle adoption, incentivizing consumers, businesses, and manufacturers to embrace sustainable transportation solutions. Legislatures generally all through the world are speeding up the shift to a cleaner, greener, and more maintainable future by setting these means in motion.

X. Resilience and Energy Independence
By reducing dependency on fossil fuels, diversifying energy sources, and facilitating the integration of renewable energy systems, electric vehicles support resilience and energy independence.These advantages have a big impact on energy security, sustainability, and the energy and transportation sectors’ resilience.
- Reduced Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Electric vehicles offer an alternative to traditional petrol and diesel vehicles, reducing dependence on fossil fuels for transportation. By shifting towards electricity as the primary energy source for vehicles, countries can decrease their reliance on imported oil and enhance their energy security.
- Diversification of Energy Sources: Electric vehicles facilitate the integration of diverse energy sources into the transportation sector. Electric vehicles can now be accused of spotless and manageable energy on account of headways in environmentally friendly power sources like sun based and wind power. This diversification reduces vulnerability to fluctuations in fossil fuel prices and supply disruptions, enhancing overall energy resilience.
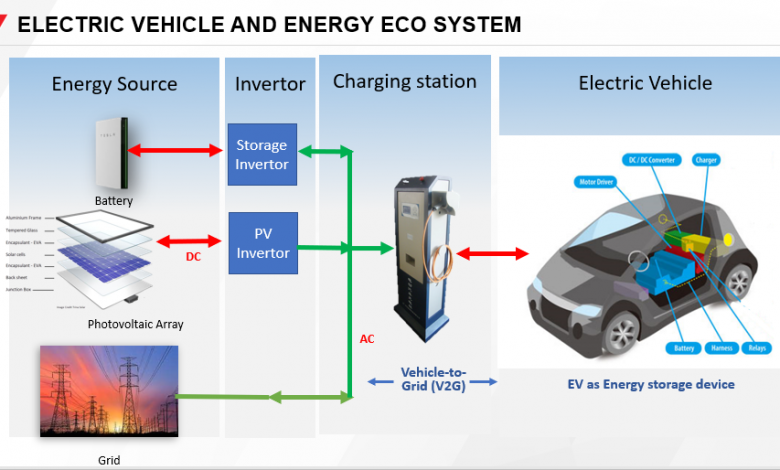
- Grid Resiliency and Vehicle-to-Grid Integration: Electric vehicles can serve as mobile energy storage units, contributing to grid resiliency. Electric vehicles can release put away energy back into the matrix on occasion of popularity or in a crisis because of vehicle-to-network (V2G) connection. This bidirectional progression of energy upgrades the adaptability and solidness of the electrical framework, further developing strength and guaranteeing a dependable energy supply.
- Decentralized Energy Generation: The widespread adoption of electric vehicles encourages the deployment of decentralized energy generation systems, such as solar panels and wind turbines. This decentralization reduces reliance on centralized power plants, making energy supply more distributed and resilient. Localized generation and consumption of renewable energy can also mitigate transmission losses and improve the overall efficiency of the energy system.
- Energy Independence: Electric vehicles contribute to national energy independence by utilizing domestically generated energy sources. Countries with abundant renewable energy resources can leverage electric vehicles to harness their own clean energy and reduce dependence on imported energy. This enhances energy sovereignty, reduces trade deficits, and strengthens the resilience of the national energy system.By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, diversifying energy sources, enabling vehicle-to-grid integration, promoting decentralized energy generation, and enhancing energy independence, electric vehicles foster resilience in the transportation and energy sectors. These developments pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable energy future, guaranteeing a steady and secure supply of electricity while reducing environmental effect.
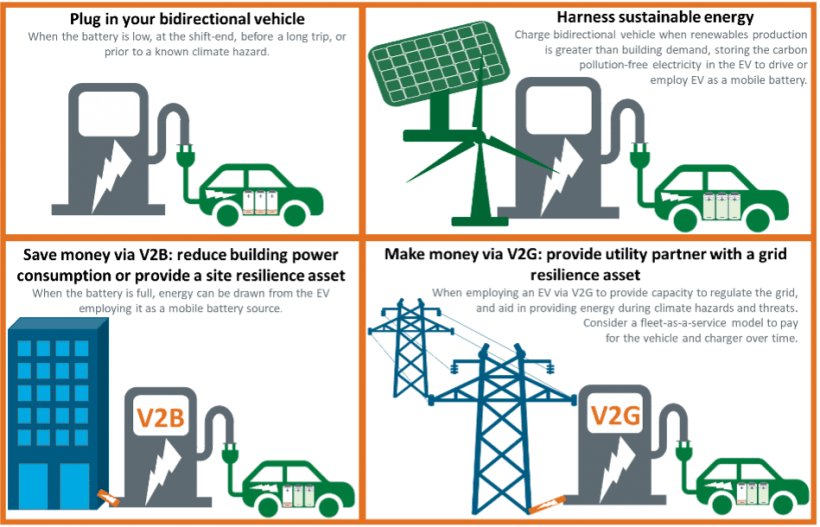
XI. Vehicle-to-Grid Integration
Creative innovation known as “vehicle-to-matrix” (V2G) joining utilizes electric vehicles’ abilities to help the electrical framework, further develop lattice solidness, and empower a more compelling energy framework.With the help of this technology, electric vehicles may now both use and return electricity to the grid as needed. Vehicle-to-Grid integration offers numerous benefits and opportunities for the energy sector and electric vehicle owners alike.
- Grid Stabilization: Electric vehicles can act as a valuable grid resource by participating in grid stabilization efforts. Electric vehicles associated with the network can deliver put away energy back into the framework during seasons of high power utilization, supporting the adjusting of market interest. This capability reduces the need for additional power plants or energy storage systems, improving grid stability and reliability.
- Demand Response: Vehicle-to-Grid integration enables demand response capabilities, allowing electric vehicles to adjust their charging and discharging patterns based on grid conditions. By leveraging smart charging technology and bidirectional communication, electric vehicle owners can respond to pricing signals or grid signals to optimize their charging and contribute to load management during peak demand periods.
- Energy Storage: Electric vehicles serve as mobile energy storage units, with their batteries capable of storing significant amounts of electricity. Electric vehicles may take in and store extra renewable energy during times when it is generated in excess, such as from solar or wind energy. This stored energy can later be utilized when renewable energy generation is low, effectively balancing intermittent energy sources and improving overall grid resilience.
- Grid Support in Emergencies: In emergency situations, electric vehicles with V2G capabilities can provide critical support to the grid. At the point when there is a blackout, they can be utilized as crisis power sources to give power to structures including houses, workplaces, and even emergency clinics. This capability enhances the resilience of the electrical grid and contributes to disaster preparedness.
- Monetization Opportunities: Vehicle-to-Grid integration creates monetization opportunities for electric vehicle owners. By participating in grid services and providing energy back to the grid, electric vehicle owners can earn financial incentives or credits, offsetting their charging costs and potentially generating additional income. This creates a mutually beneficial relationship between electric vehicle owners, grid operators, and energy markets .Vehicle-to-Grid integration represents a significant advancement in the synergy between the transportation and energy sectors. By utilizing the energy storage capacity of electric vehicles and leveraging smart charging technologies, V2G integration contributes to grid stability, enables demand response, facilitates energy storage, provides emergency power support, and creates monetization opportunities. By maximising the advantages of electric vehicles for both individuals and the larger grid ecology, this integration lays the path for a more adaptable, robust, and sustainable energy system.
XII. The Role of Electric Vehicles in Urban Planning
Urban planning methods are being significantly shaped by electric vehicles (EVs), which are also encouraging sustainable, livable communities. As cities worldwide grapple with challenges related to pollution, congestion, and carbon emissions, integrating electric vehicles into urban planning offers numerous benefits and opportunities.
- Reduced Emissions and Air Quality Improvement: Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, mitigating air pollution in urban areas. Urban communities might upgrade air quality, lower ozone depleting substance outflows, and give better everyday environments to their residents by changing to electric portability.
- Noise Reduction: Electric vehicles operate more quietly compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This decrease in noise pollution makes streets quieter and improves the standard of living throughout metropolitan regions, particularly in locations with a high concentration of people.
- Infrastructure Development: The integration of electric vehicles into urban planning necessitates the development of charging infrastructure. This infrastructure includes public charging stations, workplace charging, and home charging solutions. By strategically deploying charging infrastructure, cities can promote EV adoption and support the needs of electric vehicle owners, ensuring convenient access to charging facilities.
- Electrification of Public Transportation: Electric transports and different types of electric public transportation offer a supportable option in contrast to traditional petroleum product controlled vehicles. Public transit systems become more energy-efficient, emit less emissions, and have better overall quality thanks to electrification. Electric buses, in particular, contribute to reduced noise pollution and improved air quality along bus routes, benefiting both passengers and residents.
- Integration with Smart City Initiatives: Electric vehicles can be seamlessly integrated with smart city initiatives, leveraging technology to optimize traffic flow, parking management, and charging infrastructure utilization. By utilizing data-driven solutions and intelligent transportation systems, cities can optimize electric vehicle charging schedules, allocate charging resources efficiently, and provide real-time information to electric vehicle owners.
- Promotion of Active Transportation: Electric bicycles and scooters, which are gaining popularity in urban areas, promote active transportation and reduce reliance on conventional vehicles for short-distance trips. These electric micro-mobility solutions offer a convenient, eco-friendly option for navigating urban environments and reducing traffic congestion.
- Collaboration with Renewable Energy Integration: The growth of electric vehicles can align with renewable energy integration efforts. Cities should look into ways to combine renewable energy sources like solar and wind power with infrastructure for recharging electric vehicles. This synergy supports the transition towards a decarbonized energy system and enhances the sustainability of urban transportation.The role of electric vehicles in urban planning extends beyond individual transportation choices. By embracing electric mobility, cities can enhance air quality, reduce noise pollution, develop necessary charging infrastructure, electrify public transportation, integrate with smart city initiatives, promote active transportation, and collaborate with renewable energy integration. These activities help in the improvement of reasonable, feasible urban communities that put an accentuation on safeguarding the climate and the government assistance of their residents.

XIII. Addressing Range Anxiety
Range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery power while driving an electric vehicle (EV), has been a concern for potential EV owners. However, advancements in technology and infrastructure have significantly addressed this issue, making range anxiety less of a barrier to EV adoption. Here are some key strategies for addressing range anxiety:
- Improved Battery Technology: Electric vehicle manufacturers have made substantial progress in battery technology, increasing energy density and extending driving ranges. Modern EVs offer longer ranges, allowing drivers to travel significant distances on a single charge. Enhanced battery performance alleviates concerns about running out of power during daily commutes or longer trips.
- Expanding Charging Infrastructure: The development of a robust and widespread charging infrastructure is crucial to alleviate range anxiety. Governments, businesses, and charging network providers are investing in the installation of public charging stations, including fast-charging options, along major highways, urban centers, and parking facilities. Access to a comprehensive charging network provides drivers with the confidence that they can recharge their EVs conveniently during their journeys.
- Expanding Charging Infrastructure: The development of a robust and widespread charging infrastructure is crucial to alleviate range anxiety. Governments, businesses, and charging network providers are investing in the installation of public charging stations, including fast-charging options, along major highways, urban centers, and parking facilities. Access to a comprehensive charging network provides drivers with the confidence that they can recharge their EVs conveniently during their journeys.
- Real-Time Range and Charging Information: Electric vehicles now come equipped with sophisticated onboard systems that provide real-time range estimates and navigation assistance to nearby charging stations. This information helps drivers plan their routes effectively, ensuring they have sufficient battery charge and access to charging infrastructure when needed. It alleviates concerns about finding charging stations and provides peace of mind during longer journeys.
- Battery Management and Energy Efficiency: EVs incorporate advanced battery management systems that optimize energy usage and extend range. These systems monitor battery performance, temperature, and energy consumption, ensuring efficient use of available power. Regenerative slowing down innovation likewise makes it conceivable to recuperate energy lost during slowing down and speed increase, expanding energy proficiency and broadening the scope of the vehicle.
- Education and Awareness: Promoting education and awareness about electric vehicles is crucial in addressing range anxiety. Providing accurate and transparent information about EV range, charging infrastructure availability, and charging times helps dispel misconceptions and build confidence among potential EV owners. Test drives, public demonstrations, and informational campaigns play a vital role in familiarizing consumers with the capabilities and benefits of electric vehicles. By combining improved battery technology, expanding charging infrastructure, fast-charging capabilities, real-time range information, battery management systems, and educational initiatives, the automotive industry and governments are effectively addressing range anxiety. These means are fundamental for supporting customer trust, advancing the reception of EVs, and laying the basis for when electric vehicles are a pragmatic and harmless to the ecosystem method of transportation for everybody.

XIV. Overcoming Initial Cost Barriers
While electric vehicles (EVs) offer numerous benefits, one common concern is the initial cost barrier associated with their purchase. However, several factors are helping to overcome this challenge and make EVs more accessible and affordable for consumers. Here are some key strategies for overcoming initial cost barriers:
- Falling Battery Prices: The cost of battery technology, a significant component of EVs, has been steadily declining in recent years. Technological advancements, economies of scale, and increased production have contributed to this reduction in battery costs. As a result, EVs are becoming priced similarly to conventional cars with internal combustion engines.
- Government Incentives: Many governments around the world offer financial incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, grants, or subsidies that directly reduce the upfront cost of purchasing an EV. Government assistance is essential for lowering the price of EVs and increasing their consumer appeal.
- Lower Operating Costs: While EVs may have a higher upfront cost compared to conventional vehicles, they often have lower operating costs over the vehicle’s lifetime. EVs typically have lower maintenance and repair expenses due to fewer moving parts and reduced reliance on fluids like oil. Moreover, EV proprietors can set aside cash over the long haul on the grounds that the expense of energy used to charge an EV is commonly more affordable than the expense of petroleum or diesel.
- Increased Model Availability: As the popularity of EVs continues to grow, automakers are expanding their electric vehicle offerings. This increase in model availability provides consumers with more choices across different price ranges, making it easier to find an EV that fits their budget and preferences.
- Leasing and Financing Options: Leasing and financing options specifically tailored for EVs are becoming more prevalent. These options often include lower down payments, competitive interest rates, and flexible terms. For those who wish to experience an EV’s advantages without committing to long-term ownership, leasing can be a desirable choice.
- Second-Hand Market: Customers now have the option to buy used electric vehicles at more reasonable prices as the used EV industry grows. The availability of reliable and well-maintained used EVs offers a cost-effective entry point for individuals who want to experience electric mobility without the higher price tag of a new vehicle.
- Second-Hand Market: Customers now have the option to buy used electric vehicles at more reasonable prices as the used EV industry grows. The availability of reliable and well-maintained used EVs offers a cost-effective entry point for individuals who want to experience electric mobility without the higher price tag of a new vehicle. By leveraging falling battery prices, government incentives, lower operating costs, increased model availability, leasing and financing options, the second-hand market, and economies of scale, the automotive industry is actively working to overcome initial cost barriers associated with electric vehicles. These tactics seek to hasten the transition to sustainable and emission-free transportation by making EVs more accessible, appealing, and inexpensive.

XV. Battery Recycling and Disposal
Electric vehicle batteries, while highly durable and long-lasting, eventually reach the end of their lifespan. Proper management of battery waste is crucial to minimize environmental impact and maximize resource efficiency. Here are key aspects of battery recycling and disposal:
- Material Recovery and Resource Conservation: Electric vehicle batteries consist of valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and other metals. Recycling these batteries allows for the recovery of these valuable resources, reducing the need for new mining and extraction activities. Recycling ensures resource conservation and supports the circular economy by reintroducing materials into the production cycle.
- Specialized Recycling Processes: Battery recycling involves specialized processes designed to extract and recover valuable metals from spent batteries. These processes typically involve mechanical and chemical methods to separate and refine battery components. Advanced technologies are continuously being developed to improve recycling efficiency and maximize material recovery rates.
- Environmental Protection: Proper recycling and disposal of EV batteries help prevent environmental contamination. Batteries contain potentially harmful materials, including heavy metals and electrolytes. By recycling batteries through approved facilities, these hazardous materials can be safely extracted, reducing the risk of soil and water pollution.
- Regulatory Compliance: Governments and regulatory bodies are establishing guidelines and regulations to ensure the proper management of battery waste. These regulations often require manufacturers and stakeholders to take responsibility for the recycling and disposal of EV batteries. Compliance with these regulations helps ensure safe and environmentally friendly practices throughout the entire lifecycle of electric vehicle batteries.
- Extended Use and Second-Life Applications: Before reaching the end of their useful life in vehicles, electric vehicle batteries can still have sufficient capacity for other applications. Repurposing these batteries for secondary use, such as stationary energy storage, allows for further utilization of their remaining capacity. This approach extends the lifespan of batteries and maximizes their value before they are eventually recycled.
- Public Awareness and Education: Promoting public awareness and education about battery recycling is essential. Informing EV owners and the general public about the importance of proper battery disposal and the availability of recycling programs encourages responsible behavior. Manufacturers, government agencies, and environmental organizations play a crucial role in educating the public and providing accessible information on battery recycling options. Battery recycling and proper disposal are integral to the sustainable lifecycle management of electric vehicle batteries. Through specialized recycling processes, resource conservation, environmental protection, regulatory compliance, secondary applications, and public awareness, the industry is striving to create a robust and efficient battery recycling infrastructure. With these initiatives, the environmental impact of electric vehicle batteries is reduced as the market for electric vehicles expands in a responsible manner.
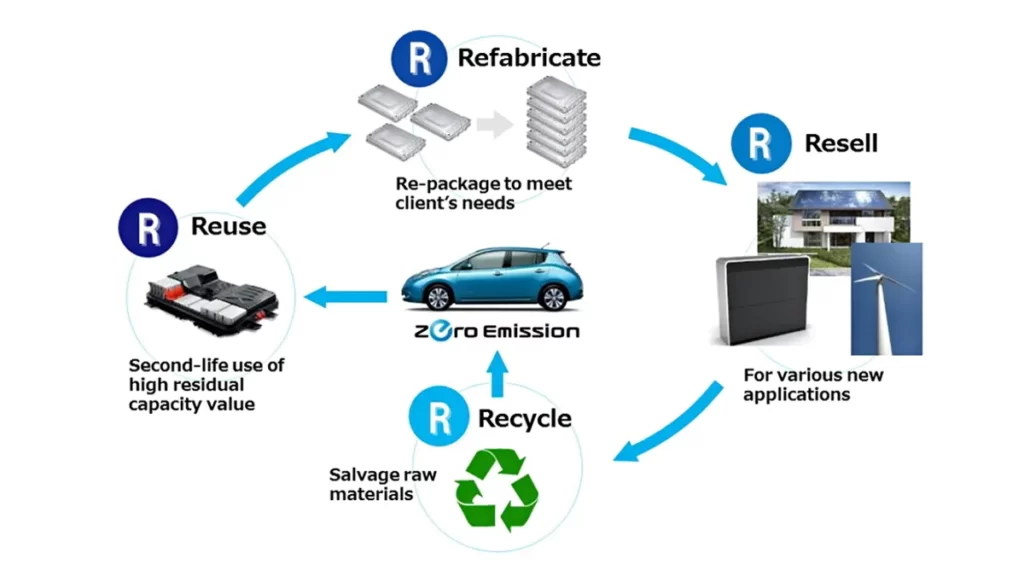
XVI. Electrifying Heavy-Duty Vehicles
Heavy-duty vehicle electrification has the potential to significantly cut emissions, enhance air quality, and advance sustainable transportation. This includes trucks, buses, and commercial fleets.Converting heavy-duty trucks to electric power has several advantages because the transportation industry produces a sizable part of greenhouse gas emissions. Here are key aspects of electrifying heavy-duty vehicles:
- Emission Reduction: Heavy-duty vehicles are major contributors to air pollution and carbon emissions. By charging these vehicles, we can radically cut ozone harming substance outflows and diminish the adverse consequences on the climate that accompany traditional diesel or petroleum engines. Zero tailpipe discharges from electric rock solid vehicles lead to cleaner air and better general wellbeing.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric powertrains offer higher energy efficiency compared to internal combustion engines. Electric heavy-duty vehicles convert a higher percentage of energy from the battery into useful work, resulting in reduced energy waste and lower operating costs. Energy efficiency gains contribute to a more sustainable and economically viable transportation sector.
- Noise Reduction: Electric heavy-duty vehicles operate more quietly than their combustion engine counterparts, reducing noise pollution in urban and residential areas. This benefit not only improves the quality of life for communities but also allows for nighttime deliveries and operations in noise-sensitive zones, contributing to more flexible and sustainable logistics.
- Improved Performance: Electric motors provide instant torque, delivering quick acceleration and responsive performance. Electric heavy-duty vehicles offer comparable or even superior performance to conventional vehicles, ensuring they meet the demanding requirements of commercial operations. With advancements in battery technology, electric heavy-duty vehicles can achieve impressive range and carry heavy payloads.
- Lower Operating Costs: Although electric heavy-duty vehicles may have higher upfront costs, they offer lower operating costs over their lifetime. Because of the way that power is regularly more affordable than diesel or petroleum, fuel costs are altogether diminished. Moreover, electric vehicles have fewer mechanical components, reducing maintenance and repair costs. The total cost of ownership for electric heavy-duty vehicles can be more favorable in the long run.
- Charging Infrastructure Development: Electrifying heavy-duty vehicles necessitates the development of a robust charging infrastructure specifically designed for commercial applications. This infrastructure includes high-power charging stations strategically located along major transportation routes, distribution centers, and depots. Investments in charging infrastructure enable reliable and efficient operations for electric heavy-duty vehicle fleets.
- Government Support: Governments worldwide are implementing policies, incentives, and regulations to encourage the electrification of heavy-duty vehicles. Financial incentives, grants, and subsidies are provided to support the adoption of electric fleet vehicles, making the transition more financially feasible for fleet operators. Regulations and pollution standards are also being devised to quicken the phase-out of heavy-duty vehicles powered by fossil fuels. By electrifying heavy-duty vehicles, we can significantly reduce emissions, improve energy efficiency, decrease noise pollution, enhance performance, lower operating costs, develop charging infrastructure, and benefit from government support. These efforts pave the way for a sustainable and greener transportation sector, transforming the way goods are transported and shaping the future of commercial transportation.

XVII. Residual Benefits of Electric Vehicles
Beyond their primary advantages such as environmental friendliness and energy efficiency, electric vehicles (EVs) offer several residual benefits that have a positive impact on various aspects of our lives. These additional benefits contribute to the overall appeal and value of electric vehicles. Here are key residual benefits of electric vehicles:
- Reduced Noise Pollution: Electric vehicles operate more quietly than conventional vehicles with internal combustion engines. The absence of engine noise and reduced mechanical vibrations make EVs significantly quieter, contributing to a more peaceful and less noisy urban environment. This effect improves both cars’ and pedestrians’ quality of life, particularly in highly populated places.
- Energy Diversity and Independence: Electric vehicles help diversify the energy sources used for transportation. By relying on electricity as a fuel instead of fossil fuels, EVs can leverage various energy generation methods, including renewables like solar and wind power. This diversification reduces dependence on finite fossil fuel resources and enhances energy independence.
- Job Creation and Economic Growth: The shift towards electric mobility stimulates job creation and economic growth. The manufacturing, maintenance, and charging infrastructure sectors associated with electric vehicles offer new employment opportunities. Moreover, the transition to EVs reduces oil imports, redirecting funds towards local industries and promoting domestic economic development.
- Health Benefits: Electric vehicles positively impact public health by reducing air pollution. By eliminating tailpipe emissions, EVs contribute to cleaner air quality, reducing the prevalence of respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. Improved air quality leads to better health outcomes and a healthier population.
- Grid Stabilization and Demand Response: Electric vehicles can serve as valuable resources for grid stabilization and demand response programs. Through smart charging and vehicle-to-grid technologies, EVs can help balance electricity demand and supply. They can advance energy use and help lattice strength by putting away abundance power during seasons of low interest and reallocating it to the framework during seasons of pinnacle interest.
- Resilience and Disaster Preparedness: Electric vehicles, with their onboard batteries, can serve as emergency power sources during natural disasters or power outages. In such situations, EVs can provide power to homes, hospitals, or critical infrastructure, ensuring access to electricity for essential needs. This capability enhances resilience and emergency preparedness within communities.
- Improved Driving Experience: Electric vehicles offer a unique and enjoyable driving experience. The instant torque provided by electric motors delivers smooth and quick acceleration, resulting in responsive and exhilarating performance. The absence of gear shifting and the regenerative braking feature further enhance the driving experience, providing a more comfortable and engaging ride.
These residual benefits of electric vehicles, including reduced noise pollution, energy diversity, job creation, health improvements, grid stabilization, resilience, and an enhanced driving experience, contribute to the widespread adoption and acceptance of electric mobility. These extra benefits further the positive effects of EVs on several facets of our lives and society at large as the electric car market continues to develop.

XVIII. Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy Synergy
The mix of electric vehicles (EVs) and environmentally friendly power sources has huge commitment for fostering a low-carbon and maintainable transportation framework. The integration of EVs with renewable energy generation offers several benefits and opportunities for a greener future. The following are significant characteristics of the interaction between electric cars and renewable energy:
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: When compared to conventional automobiles, electric vehicles driven by renewable energy sources have no tailpipe emissions, which significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions. We can efficiently decarbonize the transportation sector and quicken the shift to a low-carbon economy by combining EVs with renewable energy production.
- Maximized Renewable Energy Utilization: Electric vehicles can act as mobile energy storage units, allowing for the efficient utilization of renewable energy. During periods of high renewable energy generation and low electricity demand, excess energy can be stored in EV batteries. This put away energy can thusly be utilized to control homes and organizations or provided once again into the network on occasion of appeal, working on the mix of environmentally friendly power into the power framework.
- Demand Response and Grid Flexibility: Electric vehicles, when connected to the grid, enable demand response programs that help balance electricity supply and demand. EVs can respond to grid signals and modify their charging patterns using smart charging and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technologies. This flexibility supports grid stability, optimizes energy usage, and reduces the need for additional power generation capacity.
- Renewable Energy Siting and Local Generation: The deployment of electric vehicle charging infrastructure can be strategically aligned with renewable energy generation sites. This synergy allows for localized and distributed charging stations powered by nearby renewable energy sources. This approach reduces transmission losses, enhances energy efficiency, and supports the development of local renewable energy projects.
- Economic Opportunities: The integration of electric vehicles and renewable energy creates economic opportunities in various sectors. The growth of EVs drives the demand for renewable energy, fostering investments in renewable energy generation capacity. This expansion places nations and regions at the vanguard of the switch to clean energy by encouraging job development, economic growth, and technical innovation.
- Public Perception and Environmental Leadership: The combination of electric vehicles and renewable energy represents a powerful symbol of environmental responsibility and sustainability. The visible connection between clean transportation and renewable energy sources enhances public perception and promotes a positive environmental image. Embracing this synergy allows individuals, organizations, and governments to demonstrate leadership in addressing climate change and fostering a sustainable future.
A road to a cleaner, more sustainable, and resilient transportation system is provided by the interaction between electric vehicles and renewable energy sources. By aligning the growth of electric mobility with renewable energy generation, we can significantly reduce carbon emissions, maximize renewable energy utilization, enhance grid flexibility, strengthen energy security, stimulate economic opportunities, and showcase environmental leadership. A cleaner and more maintainable future for people in the future is made conceivable by this comprehensive methodology.

XIX. Addressing Charging Infrastructure Challenges
Electric vehicle (EV) adoption depends on a reliable and easily accessible charging infrastructure being available. While significant progress has been made in developing charging networks, several challenges remain. Addressing these challenges is crucial to ensure convenient and reliable charging options for EV owners. Here are key aspects of addressing charging infrastructure challenges:
- Expansion and Accessibility: One of the primary challenges is expanding the charging infrastructure to meet the growing demand for EVs. This involves deploying charging stations in residential areas, commercial zones, workplaces, public parking facilities, and along highways. Prioritizing accessibility ensures that EV owners have convenient access to charging infrastructure, eliminating range anxiety and promoting widespread EV adoption.
- Charging Speed and Technology: Enhancing charging speed and deploying fast-charging technologies is essential for optimizing the charging experience. DC fast chargers are one type of fast-charging station that can deliver a sizable charge in a short amount of time, minimising waiting periods for EV owners. Continued advancements in charging technology, including ultra-fast charging and wireless charging, further enhance convenience and user experience.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Standardizing charging connectors, protocols, and payment systems is critical for interoperability among different charging networks and EV models. This allows EV owners to charge their vehicles at any charging station, regardless of the charging network operator. Promoting interoperability simplifies the charging process, encourages competition, and ensures a seamless experience for EV users.
- Charging Infrastructure Planning: Strategic planning of charging infrastructure is crucial to optimize its deployment and utilization. This includes conducting feasibility studies, analyzing charging patterns, and identifying high-demand areas. Collaborating with local governments, utilities, and private stakeholders facilitates effective planning, ensuring that charging infrastructure is deployed where it is most needed.
- Investment and Funding: Adequate investment and funding are essential for expanding and upgrading the charging infrastructure. Governments, private companies, and utilities should collaborate to allocate resources for the installation of charging stations, including both public and private investments. Financial incentives, grants, and subsidies can encourage the development of charging infrastructure, making it an attractive investment opportunity.
- Smart Grid Integration: Integrating charging infrastructure with smart grid technologies enables efficient management of electricity demand and supply. Smart charging solutions can optimize charging times based on grid conditions, renewable energy availability, and electricity prices. Vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology allows bidirectional energy flow between EVs and the grid, supporting grid stability and enabling the use of EVs as a valuable energy resource.
- Public Awareness and Education: Educating the public about the benefits and availability of charging infrastructure is crucial for EV adoption. Raising awareness about the location of charging stations, different charging options, and the convenience of EV ownership helps dispel misconceptions and encourages more individuals to switch to electric vehicles. Public awareness campaigns and informative materials play a vital role in promoting EVs and the charging infrastructure.
By addressing the challenges related to charging infrastructure expansion, accessibility, charging speed, interoperability, planning, investment, smart grid integration, and public awareness, we can overcome barriers to widespread EV adoption. Collaborative efforts involving governments, utilities, private companies, and the public are crucial for building a comprehensive and reliable charging infrastructure network. By doing so, we create an environment that supports and encourages the transition to electric mobility, fostering a sustainable and cleaner transportation future.

Summary
The transition from petrol and diesel vehicles to electric vehicles (EVs) brings about numerous advantages and benefits across various aspects. In this comprehensive article, we have explored why electric vehicles are better than petrol and diesel alternatives. The key points covered include:
- Environmental Impact: EVs significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and combat climate change.
- Economic Advantages: EVs offer lower operating costs, potential savings on fuel expenses, and job creation opportunities in the growing electric vehicle industry.
- Energy Efficiency: EVs convert more energy from the battery into useful work, resulting in reduced energy waste and greater efficiency.
- Performance and Driving Experience: Electric motors provide instant torque, delivering quick acceleration and a smooth, responsive driving experience.
- Public Health Benefits: EVs help improve air quality by producing zero tailpipe emissions, reducing respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
- Technological Advancements: EVs drive innovation, fostering advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and vehicle-to-grid integration.
- Range and Charging Infrastructure: Improvements in EV range and the expansion of charging infrastructure address the concerns of range anxiety.
- Government Policies and Incentives: Governments worldwide are implementing policies and incentives to promote EV adoption, including financial support and emission regulations.
- Resilience and Energy Independence: EVs contribute to energy independence, grid stability, and can serve as emergency power sources during outages.
- Vehicle-to-Grid Integration: EVs can support the electricity grid, providing demand response and grid stabilization through bidirectional energy flow.
- Urban Planning: EVs play a role in sustainable urban planning, reducing congestion, and promoting smart city initiatives.
- Addressing Range Anxiety: Strategies like improved charging infrastructure, battery advancements, and public education help alleviate concerns about EV range.
- Overcoming Initial Cost Barriers: EV prices are becoming more competitive over time, and government incentives assist in reducing the initial cost barrier.
- Battery Recycling and Disposal: Proper battery recycling and disposal processes ensure the environmental sustainability of EVs.
- Electrifying Heavy-Duty Vehicles: The electrification of trucks, buses, and commercial fleets brings emission reductions, energy efficiency, and economic benefits.
- Residual Benefits: EVs provide additional advantages such as reduced noise pollution, energy diversity, job creation, and enhanced driving experience.
- Electric Vehicles and Renewable Energy Synergy: The integration of EVs with renewable energy maximizes energy utilization, reduces carbon emissions, and strengthens the grid.
- Addressing Charging Infrastructure Challenges: Expanding and improving charging infrastructure accessibility, speed, interoperability, planning, investment, and public awareness are crucial for widespread EV adoption.
By understanding these advantages and addressing the challenges, we can pave the way for a sustainable transportation future. A greener and healthier earth is made possible by electric vehicles, which provide a cleaner, more technologically sophisticated alternative to conventional petrol and diesel automobiles .The switch to electric vehicles is gaining speed and influencing the mobility of the future thanks to ongoing developments and support from corporations, governments, and individuals.

FAQs
Q1: How far can electric vehicles travel on a single charge? A1: A variety of variables, including battery capacity, road conditions, and vehicle efficiency, affect an electric car’s range. The typical driving distance of contemporary electric vehicles is somewhere in the range of 240 and 480 kilometers (150 to 300 miles). However, this range is continuously improving as battery technology advances.
Q2: How long does it require for an electric vehicle to charge? A2: Depending on the charging method used and the battery size of the car, different charging times apply to electric vehicles. Level 1 charging, using a standard household outlet, can take several hours to fully charge an EV. Level 2 charging stations, typically installed at homes and public locations, can charge an EV in 4-8 hours. DC fast chargers, found along highways and public charging networks, can provide a significant charge in around 30 minutes to an hour.
Q3: Is it expensive to charge an electric vehicle? A3: Charging an electric vehicle is generally cheaper than refueling a petrol or diesel vehicle. The cost of electricity for charging depends on local electricity rates and the charging infrastructure used. Charging at home is usually more affordable compared to public charging stations. Additionally, some regions offer discounted electricity rates during off-peak hours, further reducing charging costs.
Q4: Are electric vehicles more expensive to purchase than petrol/diesel vehicles? A4: Electric vehicles traditionally had higher upfront costs due to battery technology and production costs. However, the price of electric vehicles has been falling due to technological developments and expanded manufacturing capacity. Government subsidies and incentives are frequently offered as well to lower the cost of electric automobiles.
Q5: How long do electric vehicle batteries last? A5: Electric vehicle batteries are designed to be durable and typically have warranties ranging from 8 to 10 years or more. A battery’s life expectancy is impacted by various factors, for example, utilization designs, charging schedules, and natural circumstances.Even after numerous long periods of purpose, with the right upkeep and care, electric vehicle batteries can hold a sizable measure of limit.
Q6: Can electric vehicles be charged at home? A6: Yes, electric vehicles can be charged at home using a Level 1 or Level 2 charging station. Level 1 charging involves using a standard household outlet and is the slowest charging option. Level 2 charging requires installing a dedicated charging unit that operates at higher power levels, resulting in faster charging times.
Q7: Are there enough public charging stations for electric vehicles? A7: The availability of public charging stations varies depending on the region. To satisfy the rising demand for electric vehicles, the infrastructure for charging is fast emerging in numerous locations. Public charging stations are commonly found in urban areas, shopping centers, workplaces, and along highways. Several online platforms and mobile apps help locate nearby charging stations.
Q8: Can electric vehicles tow trailers or carry heavy loads? A8: Yes, many electric vehicles have towing capabilities and can handle trailers or carry heavy loads. However, towing or carrying heavy loads may impact the vehicle’s range and efficiency. It is advisable to consult the vehicle’s specifications and recommendations from the manufacturer regarding towing capacity and load limits.
Q9: Do electric vehicles require regular maintenance? A9: Electric vehicles generally require less maintenance compared to petrol or diesel vehicles. They have fewer moving parts, eliminating the need for oil changes and certain mechanical repairs. However, regular maintenance such as tire rotations, brake inspections, and battery system checks are still necessary.
Q10: Can electric vehicles be charged with renewable energy? A10: Indeed, electric vehicles can be accused of power created from sustainable power sources, for example, sun based, wind, or hydroelectric power.
Q11: Can electric vehicles be driven in extreme weather conditions? A11: Electric vehicles can be driven in extreme weather conditions, including hot summers and cold winters. However, extreme temperatures can affect the vehicle’s range and performance. Electric vehicles often have advanced thermal management systems to maintain optimal battery temperature, ensuring efficient operation in various weather conditions.
Q12: Can electric vehicles be charged at fast-food restaurants or shopping malls? A12: Many fast-food restaurants, shopping malls, and other public locations are installing charging stations to cater to electric vehicle owners. These charging stations allow EV proprietors the opportunity to charge their vehicles while they go out to shop, eat, or do different things. The availability of charging stations at such establishments continues to increase as electric vehicle adoption grows.
Q13: Can electric vehicles generate electricity for homes during power outages? A13: Electric vehicles may be able to recharge the grid or power houses during blackouts thanks to vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology. However, widespread implementation of V2G is still in the early stages, and it requires compatible infrastructure and vehicle support. V2G holds promise for future energy solutions and grid resiliency.
Q14: Are there incentives or subsidies available for purchasing electric vehicles? A14: Many governments worldwide offer incentives and subsidies to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. These incentives can include financial rebates, tax credits, grants, and access to carpool lanes or toll discounts. Contingent upon the country, state, or nearby government, these motivating forces might possibly be offered and to what sum.
Q15: Can electric vehicles be charged using solar panels at home? A15: Yes, it is possible to charge electric vehicles using solar panels installed at home. This setup, known as solar PV (photovoltaic) charging, allows for sustainable and clean charging. Daylight is changed over into power by sunlight based chargers, which can then be utilized to re-energize an electric vehicle’s battery. It provides an environmentally friendly option and can further reduce the overall carbon footprint of electric vehicle usage.
Q16: Can electric vehicles be used for long-distance travel? A16: Yes, electric vehicles can be used for long-distance travel, thanks to the growing network of charging infrastructure. With careful planning and utilizing fast-charging stations along the route, it is feasible to travel long distances in an electric vehicle. Long-distance travel has become more convenient as battery technology continues to evolve, increasing range and charging speed.
Q17: Are electric vehicles quieter than petrol or diesel vehicles? A17: Yes, electric vehicles are generally quieter than petrol or diesel vehicles. The absence of an internal combustion engine results in reduced noise levels, providing a more serene driving experience and contributing to noise pollution reduction in urban areas.
Q18: Can electric vehicles help reduce dependence on imported oil? A18: Yes, electric vehicles can play a significant role in reducing dependence on imported oil. By shifting to electric vehicles powered by locally generated electricity, countries can decrease their reliance on fossil fuels for transportation, contributing to energy independence and reducing oil imports.
Q19: Can electric vehicles be charged at workplaces? A19: Yes, many workplaces are now installing charging stations to accommodate electric vehicle owners. Charging at workplaces allows EV owners to conveniently charge their vehicles during working hours, further extending their driving range and reducing the need for additional charging stops.
Q20: Can electric vehicles be used in rural areas with limited charging infrastructure? A20: While charging infrastructure in rural areas may currently be more limited compared to urban areas, the availability of home charging and the expansion of charging networks are making electric vehicles viable in rural areas as well. Home charging provides a reliable and convenient option for EV owners, and efforts are being made to expand charging infrastructure in rural communities. Additionally, advancements in fast-charging technologies and the establishment of charging networks along major highways are improving accessibility for electric vehicle users in rural areas. It is anticipated that charging infrastructure will spread as demand for electric vehicles rises, making electric vehicle ownership practical and convenient in remote locations as well. By addressing typical questions and highlighting the advantages and viability of owning and operating an electric vehicle,
these FAQs offer insightful information on the practical aspects of electric vehicles. The switch to electric vehicles grows more alluring as technology develops and the availability of charging stations increases since they provide a cleaner, more environmentally friendly, and economically viable transportation option.
3 thoughts on “Why Electric Vehicles Are Better Than Petrol And Diesel”